























STEM CELL
We contribute to promoting human health.
We are the global leader in stem cell therapies



Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that are not completely differentiated, and are cells that have the ability to differentiate into specific tissue cells. While normal cells increase the number of individuals through division, stem cells have the ability to make various cells and tissues such as brain, skin, cartilage, bone, nerve and muscle through division and differentiation.

The Characteristics of Stem Cell
Homing Effect: Stem cells are able to self-locate and regenerate damaged parts of the body.
Self-Renewal: Stem cells can replicate into cells that have the same morphology and ability.
Multipotential: Stem cells in an undifferentiated state can differentiate into various tissues and organs, such as the heart, bone, nerves, skin, and liver.
Homing Effect: Stem cells are able to self-locate and regenerate damaged parts of the body.
Self-Renewal: Stem cells can replicate into cells that have the same morphology and ability.
Multipotential: Stem cells in an undifferentiated state can differentiate into various tissues and organs, such as the heart, bone, nerves, skin, and liver.
The Type of Stem Cell
Embryonic Stem Cell: Embryonic stem cells that are less than 14 days old and have not been modified by oocyte and spermatozoon can be grown into numerous kinds of cells and tissues.
Adult Stem Cell: Undifferentiated cells existing in various tissues of the human body can be harvested from bone marrow, adipose, umbilical cord blood, etc., and differentiated into necessary tissues.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell: These stem cells have been created by manipulating the genes of fully grown specific somatic cells, and degenerating cell differentiation.
Embryonic Stem Cell: Embryonic stem cells that are less than 14 days old and have not been modified by oocyte and spermatozoon can be grown into numerous kinds of cells and tissues.
Adult Stem Cell: Undifferentiated cells existing in various tissues of the human body can be harvested from bone marrow, adipose, umbilical cord blood, etc., and differentiated into necessary tissues.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell: These stem cells have been created by manipulating the genes of fully grown specific somatic cells, and degenerating cell differentiation.
Regeneration of damaged cells.
Regeneration of damaged blood vessels to help blood supply.
The damaged cells are differentiated and regenerated into normal cells.
The immune system function is improved by increasing the immunity of immune system organs.
The growth factors of hormones, collagen, etc., are promoted to regenerate tissue in the body.
Cell death is prevented in the body.
Maintains a balance between Th1 / Th2

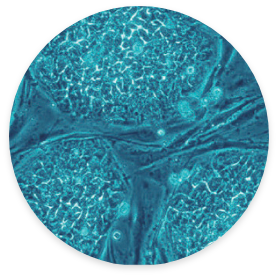

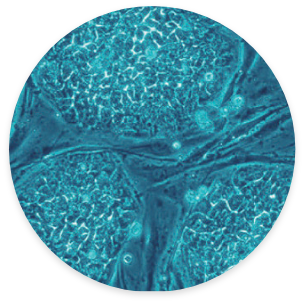
Embryonic Stem Cell
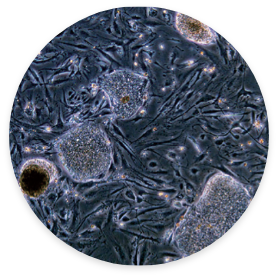

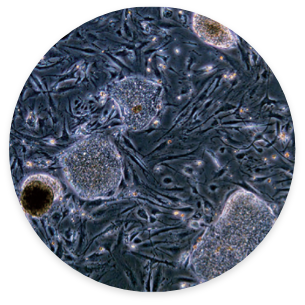
Adult Stem Cell
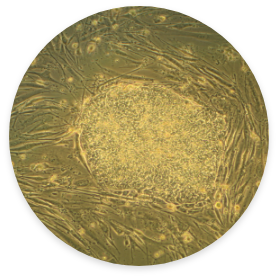

Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell
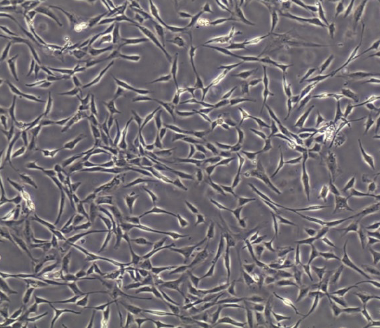


It is the most easy way to obtain and isolate abundant amount of adult stem cells, and also it shows stable proliferation and growth rate with great differentiate potential which can differentiate into almost all cell types.



Cells from own body has very rare possibility to cause an immune response which can ensure safety for the patient from unwanted immune reactions or genetic modifications.

Blood vessels distribute blood throughout the body. Circulating stem cells in blood vessels are able to reach the damaged tissue and promote tissue repair. Thus, the intravenous injection of stem cells can result in beneficial outcomes in the area that direct injected stem cells will probably not reach.