























IMMUNE CELL
We contribute to promoting human health.
We are the global leader in stem cell therapies


Immunity is the defense of one's body against foreign substances and self-derived substances. It removes foreign substances to acquire immunity and eliminates cancer cells and waste to maintain health. However, if the immunity is insufficient, chronic infectious diseases, cancers, etc. occur and if the immunity is excessive, it leads to allergic or autoimmune diseases. Immune cells are divided into macrophages, NK cells, B cells which are involved in innate immunity, and T cells, B cells involved in acquired immunity, and dendritic cells, and gamma delta T cells, which are involved in both immunity.
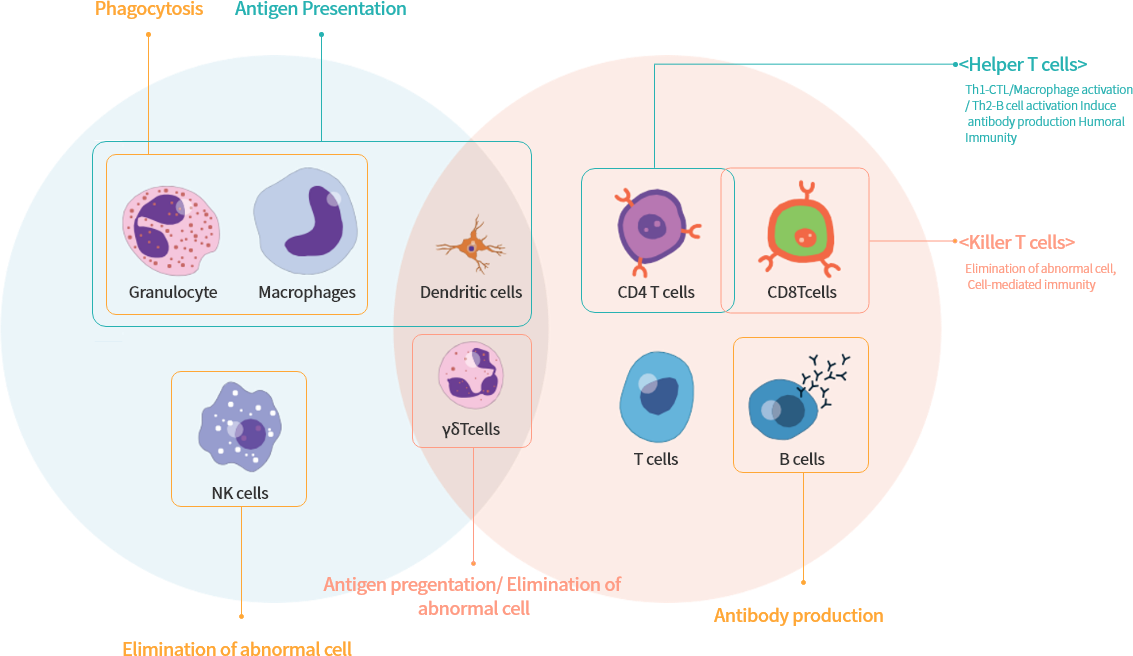

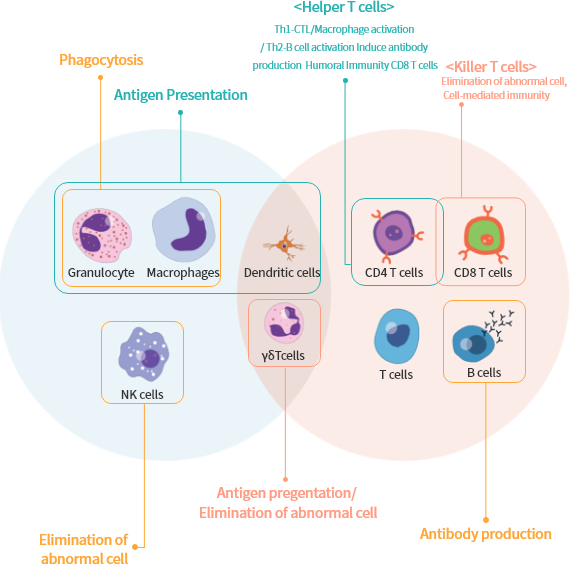
Innate Immune cells
Phagocytosis
Abnormal cell killing
Phagocytosis
Acquired immune cells
CD8 T cells
CD4 T cells
Antibody production (Induction of humoral immune response)
Killer T cells : Abnormal cell killing(Induction of cellular immune response)
Helper T cells : Th1 - Activation of CTL and macrophages
Th2 - Differentiation of B cells and induction of antibody production
Innate&Acquired immune cells
Antigen present
Antigen present, Abnormal cell killing
NK cells
Attack cells infected with viruses, or tumor cells
Macrophages
Phagocytosis of bacteria, treatment of foreign objects and waste, antigen presentation, anti-viral, anti-cancer treatment
iNKT cells
Immune regulation and immunity enhancement in various immune diseases
Dendritic cells
The most potent of antigen presenting cells against cancer cells
B lymphocytes
Antibody production
T lymphocytes
Tissue-compatible antigen binding to attack tumor cells